-
Learn the Basics
-
- Spaces
- Space Types
- Creating Spaces
- Adding Users to Spaces
- Space Activity Stream
- Following Spaces
- Space Details
- General Space Settings
- Duplicating Spaces
- Renaming Spaces
- Changing the Space Color and Icon
- Removing Users from Spaces
- Closing and Restoring Spaces
- Moving Spaces between Different KanBo Environments
- Deleting Spaces
-
- Creating Cards
- Following Cards
- Scheduling Cards
- Renaming Cards
- Duplicating Cards
- Quick Actions
- Mass Actions
- Copy & Paste
- Archiving Cards
- Adding Cards to MySpace
- Adding Mirror Cards
- Removing Mirror Cards
- Moving Cards between Spaces
- Deleting Cards
- Removing Cards from MySpace
- Hinzufügen von Karten zu "MySpace"
- Entfernen von Karten aus "MySpace"
- Hinzufügen von Status
-
Visualize Work
-
- Space Views
- Creating Space Views
- Personal and Shared Space Views
- Card Grouping
- Filtering Cards
- Display Settings
- Work Progress Calculation
- Grouping Description
- Card Grouping Settings
- Changing the Order of Groupings
- Changing the Order of Space Views
- Deleting Space Views
- Following Card Statuses and Custom Fields
-
-
Collaborate
-
Level Up Your Work
-
Work Securely
-
Integrations
-
- Advanced KanBo Actions in Power Automate
- Creating KanBo Space Attached to Subfolder Created by Power Automate
- Creating Document Folders in Document Libraries Created by KanBo with Power Automate
- Exporting Space Views to Excel
- KanBo and Azure Logic Apps Integration
- Power Automate Integration: Triggers and Actions
- Seamless Import from Microsoft Planner to KanBo
- Synchronizing KanBo with Outlook Calendar
- Using KanBo Outlook App
-
Search Commands
This post is also available in: Deutsch
Search commands are special characters that can be used in a KanBo Search query. They are useful for finding results that match a particular pattern, or for dealing with spelling variations or incomplete information.
Unlike the usual search, capitalization matters when you use search wildcard operators.
Special characters are: ?, *, ” “, ~, +, –, AND, OR.
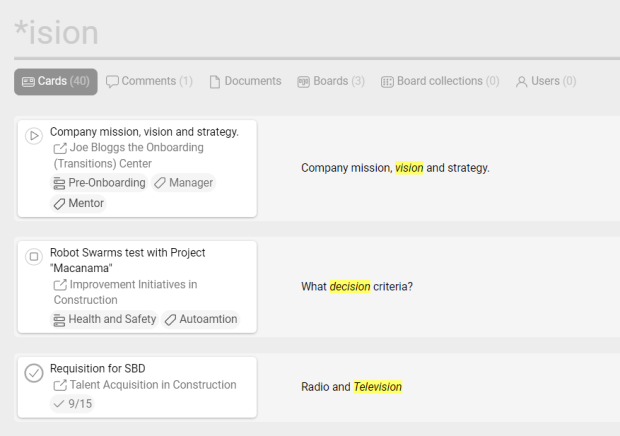
?
Wildcard searches can be run on individual terms, using “?” to replace a single character.
Really helpful when you are not sure about spelling. Instead of looking twice or more, try to replace an uncertain letter with a question mark. You can use it multiple times in one query.
Examples:
- m?n?ger
- organi?ational
*
" "
Use quotation marks to exclude synonyms and get exact phrase you need to find.
Example: “KanBo is”
+
With a plus sign, you can specify those words that must necessarily be included in the search results.
Example: event +meeting
AND
When you are interested only in outcomes containing both words.
Example: important AND meeting
OR
Use it to get results related to the first, the second, or both phrases.
Example: CV OR resume
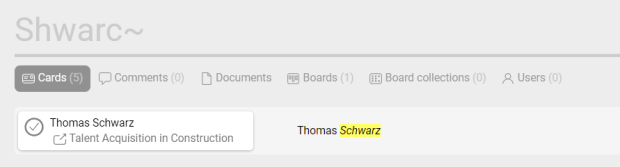
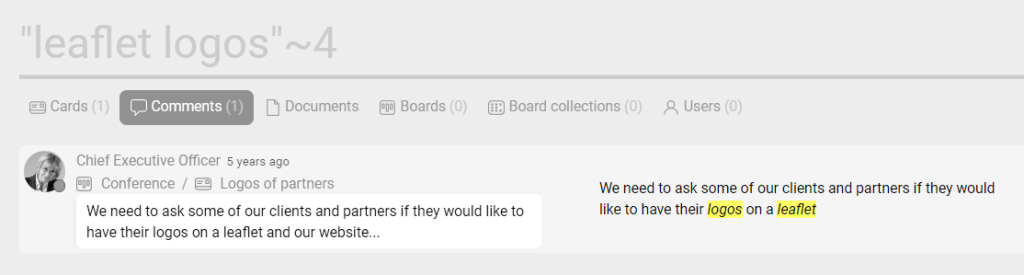
Proximity search "x y" ~z
Useful when you want to narrow down your query. After the “~” operator, specify the space between words. Proximity limitation helps to avoid search results with words spread in unrelated documents, notes, comments, etc.
The word order doesn’t matter.
Examples:
- “digital conference” ~2
- “leaflet logos” ~4
If you need to use any of the special characters in your query itself, you should remember about escaping them with a leading backslash mark "\".
Example: to search for the phrase (1+1)=2, you have to write your query as \(1\+1\)\=2.
The reserved characters are: + - = && || > < ! ( ) { } [ ] ^ " ~ * ? : \ /
FAQ
What are the options to specify my search results?
Try to use search filters to narrow down your search results. You can use search commands to precise your query. Change search sorting if the date is significant in this query.
Can I use KanBo Search in only one specific space?
Yes, you can limit your scope to the current space by ticking the box on the right.
Was this article helpful?
Please, contact us if you have any additional questions.